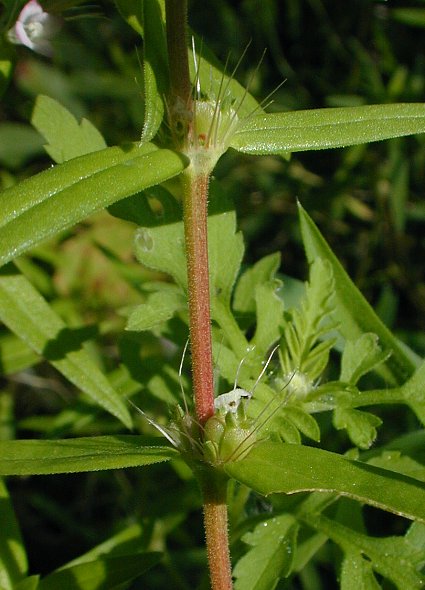
Description: This herbaceous plant is a summer annual that has stems about ½–1' long. These stems are usually erect or ascending, although sometimes they sprawl across the ground. The stems are unbranched or sparingly branched, light green to red, bluntly 4-angled (at least above), and short-pubescent (var. teres) to hairy (var. setifera). Pairs of opposite leaves occur along the entire length of each stem. These leaves are up to 1½" long and ¼" across; they are linear, linear-lanceolate, or linear-oblong in shape, entire (toothless) and involute (rolled downward) along their margins, and sessile with prominent central veins. The upper leaf surface is medium green and appressed short-pubescent to glabrous, while the lower leaf surface is slightly more pale and short-pubescent primarily along the central vein. The leaf bases along each stem are joined with merged stipules that form shallow cup-like structures. The exterior of these stipules is green to whitish green and sparsely short-pubescent to hairy. Along the upper rim of each pair of merged stipules, there are long erect bristles up to ½" long; these bristles are light green, white, or red.
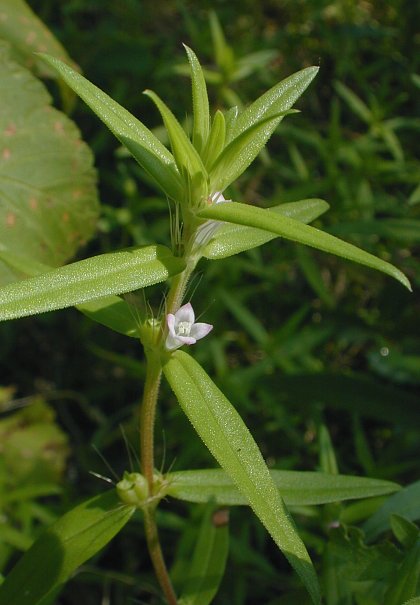

Either solitary or
small clusters of 2-3 flowers are produced from
the axils of the middle to upper leaves. Each flower is up to ¼"
long, consisting of a tubular-funnelform corolla with 4 spreading
lobes, 4
green sepals that are lanceolate in shape, 4 stamens with pale yellow
to white anthers, and an inferior ovary with a single white style. The
corolla is lilac, pink, or white; its exterior is often finely
short-hairy. The sepals are sparsely short-pubescent to hairy; they are
shorter
than the corolla. The style has a knobby (capitate) tip. Both the
stamens and style are included or only
slightly exserted from the corolla. The blooming period occurs from
mid-summer to early autumn, lasting about 1-2 months. There is no
noticeable floral scent. Afterwards, the flowers are replaced by dry
fruits (schizocarps) that are obovoid in shape with remnants of the
persistent sepals at their apices. Immature fruits are green, while
mature fruits are brown. These fruits are sparsely short-pubescent (var. teres)
to hairy (var. setifera);
their fine hairs are straight and ascending.
Eventually, these fruits divide into 2 nutlets each. The nutlets are
about 3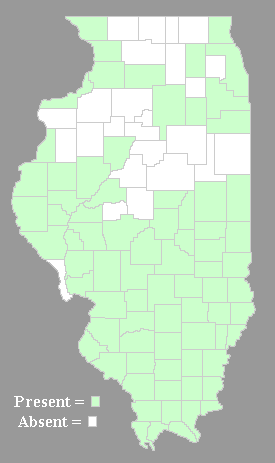 mm. (1/8") long,
half-obovoid in
shape, brown, and more or less
covered with persistent fine hairs. The root system consists of a
slender taproot with secondary feeder roots. This plant often forms
colonies by reseeding itself.
mm. (1/8") long,
half-obovoid in
shape, brown, and more or less
covered with persistent fine hairs. The root system consists of a
slender taproot with secondary feeder roots. This plant often forms
colonies by reseeding itself.
Cultivation:
The preference is full sun, dry conditions, and poor soil containing an
abundance of sand, gravel, or compacted clay. This plant will also
tolerate partial sun and moister conditions with fertile soil, in which
case it will be displaced by taller plants eventually. Drought
tolerance is quite good because of the long taproot.
Range & Habitat:
Rough Buttonweed occurs occasionally in the southern half of Illinois,
where it is native, and a few counties in the northern half, where it
is probably adventive. Illinois lies along the
northern range limit of this species. Habitats include upland
prairies where there is sparse vegetation, hill prairies, sand
prairies, rocky glades, gravel bars along rivers, pathways with
compacted soil, gravelly areas along roadsides, gravelly
areas along railroads, and barren waste ground. Areas with a
history of disturbance are preferred. Rough Buttonweed is regarded as a
common weed in the southern states, but it is less ubiquitous in
Illinois.
Faunal Associations:
Limited information is available about this plant's relationships to
various fauna. The nectar and pollen of the flowers probably attract
small bees and flower flies (Syrphidae). It has been reported by Tietz
(1972) that caterpillars of the Tersa Sphinx (Xylophanes
tersa) feed on Rough Buttonweed. This moth has a southern
distribution, but it is a strong flyer that migrates to the northern
states during the summer. Another insect that feeds on this plant is a
flea beetle, Strabala
rufa (Clark et al., 2004). This flea beetle has a brownish
orange to red carapace. The Greater Prairie Chicken eats the seeds, and
possibly other gamebirds feed on them as well.
Photographic Location:
The photographs were taken of plants growing on a little-used path with
compacted soil. This path was located near an abandoned railroad in
Champaign County, Illinois. Rather large colonies of Rough Buttonweed
occurred in this area, primarily in sunny areas where Partridge Pea (Chamaecrista
fasciculata) and Flowering Spurge (Euphorbia
corollata) also occurred. The photographed plants are the
less
hairy variety of Rough Buttonweed, Diodia
teres teres.

Comments:
Rough Buttonweed (Diodia
teres) is not particularly showy and it is
easily overlooked. This plant resembles some of the other buttonweeds
(Diodia spp.),
but it has more narrow leaves and it prefers to grow in
drier, sunnier places. Compared to Smooth Buttonweed (Diodia
virginica), Rough Buttonweed has shorter
flowers, undivided
styles, and corollas that are often lilac or pink. Smooth Buttonweed
has white flowers with slender divided styles. Other common names of Diodia teres
are 'Poorjoe' and 'Poverty Weed.' These are primarily
southern names that refer to this plant's preference for poor soil.
There are two varieties of Rough Buttonweed: the typical variety (var.
teres) and a more hairy variety (var. setifera).
This latter variety
occurs in southern Illinois.