Description: This herbaceous perennial plant is 1-4' tall, branching occasionally. The stems are square or round, and usually pubescent where new growth occurs, becoming glabrous with age. The hairless leaves are opposite or alternate along the stems, sessile or with short petioles, and up to 4" long and ½" across. They are narrowly lanceolate in shape, and sometimes have purple veins or spots. There are 4-8 teeth per centimeter along the margin of each leaf.

From the upper axils of some
of the upper leaves, there appears a single flower with a long calyx
tube on a short stalk (peduncle). This calyx tube is pubescent and more
or less erect, terminating in 4 lanceolate sepals that often tinted
purple or pink. These sepals are a little shorter than the petals. The
4 notched petals are white or light pink, and span about 1/3" across.
At the throat of the flower, there is a prominent pistil that is often
knobby at the end, which is surrounded by several stamens. These
flowers bloom for about a month during late summer or early fall. The
calyx tube matures into an elongated seed capsule, which splits open to
release a multitude of tiny seeds with small tufts of reddish brown
hair. These seeds are distributed by the wind. The root system is
fibrous and produces rhizomes, which enables this plant to spread
vegetatively.
Cultivation:
The preference is full sun to light shade, and wet to moist conditions.
The soil should contain lots of organic material to retain moisture.
The foliage is rather fragile and can become damaged easily. This plant
tolerates occasional flooding, and prefers rather cool conditions.
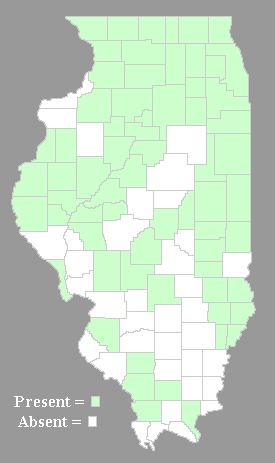
Range & Habitat:
The native Cinnamon Willow-Herb occurs occasionally in northern and
central
Illinois, but it is uncommon or absent in the southern section of the
state. Its range
extends further to the south than other Epilobium spp.,
which are usually restricted to northern Illinois. Habitats include
poorly drained areas of black soil prairies, moist woodlands, woodland
borders, and various kinds of wetlands, including marshes, bogs, fens,
seeps, and edges of ponds, rivers, or drainage ditches. The Willow
Herbs are pioneer species that thrive on some kind of disturbance, such
as fire.
Faunal Associations:
The flowers probably attract bees and flower flies, which seek nectar
and pollen. The caterpillars of various moths eat the foliage of
Willow-Herbs, including Hyles lineata (White-Lined
Sphinx), Eudryas unio (Pearly Wood Nymph), Anticlea
multiferata (Many-Lined Carpet), and Scythris
magnabella (Scythridid Moth sp.). The seeds are too small to
be of much interest to birds. The foliage is non-toxic and occasionally
eaten by mammalian herbivores, but it has low food value.
Photographic Location:
A poorly drained area of prairie in Meadowbrook Park, Urbana, Illinois.
Comments:
The flowers are rather small-sized, but they are often produced in
abundance on large plants. The most distinctive characteristic of
Cinnamon Willow-Herb is the reddish brown coloration of the tufts of
hair on the seeds, which is responsible for the common name of this
plant. Other Epilobium spp. have tufts of hair that
are white or faded brown or grey. Cinnamon Willow-Herb also has
serrated leaves with 4-8 teeth per centimeter, while other Willow-Herbs
have leaves with either smooth edges or fewer teeth per centimeter. An
unusual characteristic of the Willow-Herbs is the long calyx-tube of
the flowers, which occurs behind the petals, and
eventually becomes an elongated seed capsule. It looks like a flowering
stalk (peduncle), but it is actually part of the flower where the
ovaries are contained. In some members of the Mustard family and
miscellaneous other plants, an elongated seed capsule develops in front
of the petals. This is one way to determine whether the plant in front
of you is a Willow-Herb, or a quite different species of plant.